Opening Hours
We are available 24/7.
Leg swelling, or edema, occurs when excess fluid accumulates in the lower limbs, causing them to swell and increase in circumference. This common symptom can be caused by a variety of diseases and disorders. Effective diagnosis and treatment of leg edema require a comprehensive understanding of its underlying causes.
Pitting edema is characterized by an indentation or “pit” that remains when pressure is applied to the affected area. This type of swelling is often seen in conditions like venous insufficiency, where damaged vein valves lead to reduced blood flow and leg swelling.
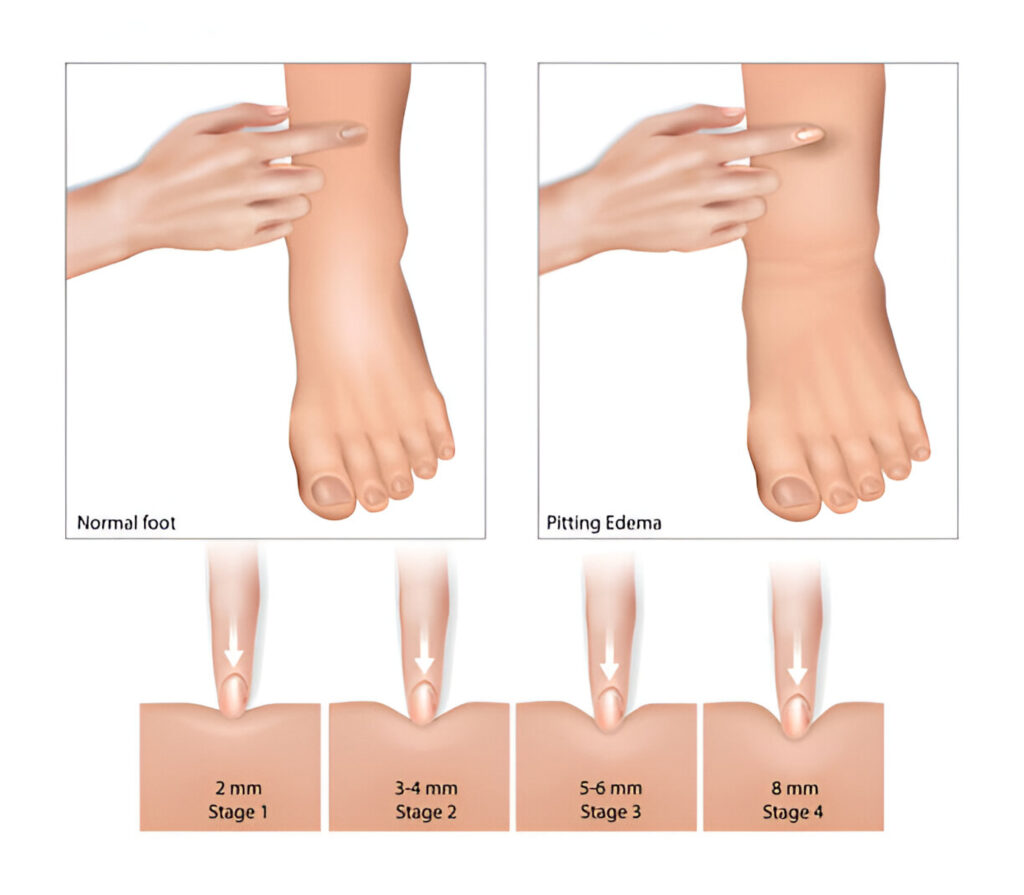
Peripheral edema involves swelling of the feet and ankles without pitting. This can be caused by various conditions, including pregnancy, heart failure, kidney disease, and liver disease.
Medical professionals use various methods to diagnose the cause of leg swelling:
The treatment for leg swelling depends on the underlying cause and may include
Minimally invasive procedures, such as angioplasty and embolization, can address the underlying cause of edema and improve blood flow.
Non-invasive or less invasive treatments can often manage swelling and improve leg health.
Pregnancy can lead to leg edema due to:
Interventional radiologists play a crucial role in treating leg edema caused by vascular issues. They use minimally invasive techniques like:
Their expertise in imaging techniques ensures accurate diagnosis and procedure guidance.
Various medications can alleviate leg pain and swelling, depending on the cause:
Treating leg swelling is essential for addressing its root cause, relieving symptoms, and improving the patient’s quality of life. Interventional radiologists provide minimally invasive techniques to enhance blood flow and reduce edema caused by vascular issues. Understanding the triggers of leg, foot, and ankle swelling is crucial for determining the most effective treatment. Preventing leg edema can help reduce symptoms, improve mobility, and avoid complications.
We are available 24/7.
©2024 kmveinvsandpainclinic . All Rights Reserved.