Opening Hours
We are available 24/7.
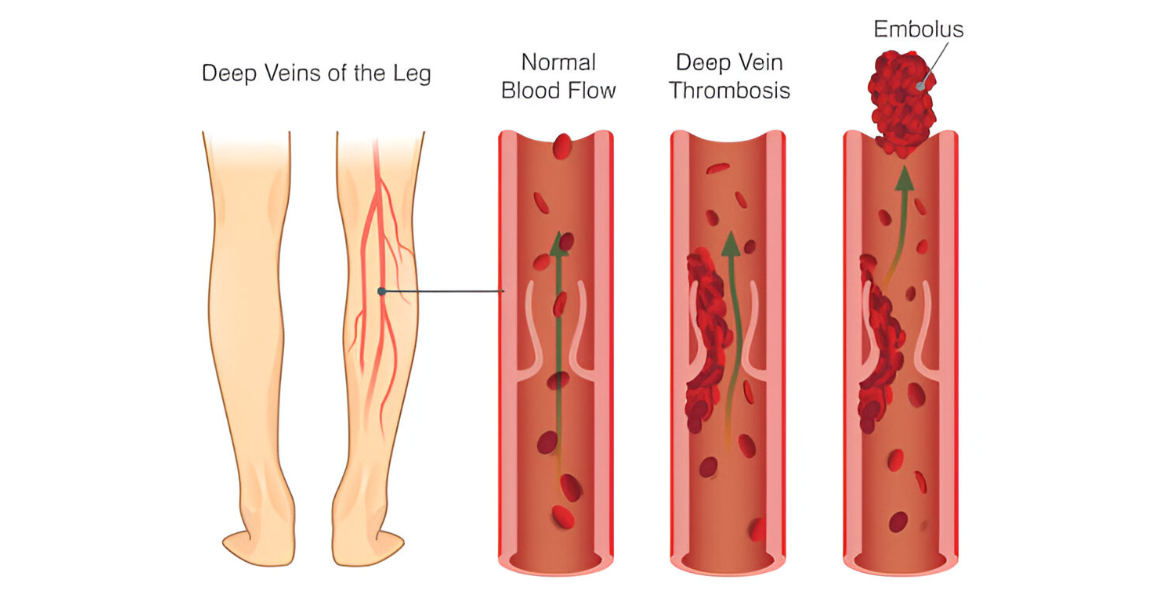
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, usually in the legs. If untreated, it can lead to serious complications like pulmonary embolism and permanent vein damage. This article provides a concise overview of DVT, including its definition, symptoms, diagnosis, causes, and risk factors. We will also cover treatment options, potential complications, recovery, and the role of interventional radiology.
Additionally, we'll discuss the costs of DVT treatment in Jaipur, the use of IVC filters and catheter-directed thrombolysis, and whether health insurance covers these treatments.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), also known as venous thrombosis, is a condition where a blood clot (thrombus) forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs but potentially in the arms, pelvis, or other parts of the body. If untreated, DVT can lead to severe complications, including pulmonary embolism (PE). PE occurs when a portion of the clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, potentially causing breathing difficulties, chest pain, or even death.
Signs and Symptoms:
Common indicators of DVT include:
Immediate medical attention is crucial if you experience any of these symptoms.
Diagnosis:
DVT is typically diagnosed using imaging techniques such as color Doppler ultrasound or computed tomography (CT). Treatment usually involves anticoagulant medications like heparin, warfarin, rivaroxaban, or dabigatran to prevent the clot from growing or new clots from forming. In cases with significant clot burden, procedures like catheter-based thrombolysis or mechanical thrombectomy might be considered.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Common causes and risk factors for DVT include:
Who is at Higher Risk?
Individuals at greater risk for DVT include:
Prevalence:
DVT is relatively common, with an estimated 300,000 to 600,000 cases occurring annually in the United States.
When to See a Doctor:
Seek medical advice promptly if you experience symptoms such as leg swelling, pain, warmth, or redness. Early intervention is key to preventing serious complications.
Treatment:
DVT treatment generally involves anticoagulant medications to prevent clot growth or travel. Compression stockings may help with swelling and improve blood flow. For severe cases, treatments like catheter-directed thrombolysis or IVC filters may be used.
Prevention:
To prevent DVT:
Complications:
If untreated, DVT can lead to serious issues like pulmonary embolism, post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS), and chronic venous insufficiency (CVI).
Recovery:
Recovery from DVT varies based on severity and treatment. Typically, anticoagulant therapy is needed for several months, and regular follow-up with your doctor is necessary to monitor your condition and adjust treatment.
DVT Risk and Knee Replacement Surgery:
Patients undergoing knee replacement surgery face an increased risk of DVT. Preventative measures like compression stockings or anticoagulants may be recommended.
Choosing the Right Treatment:
The optimal treatment for DVT depends on its severity and the patient’s overall health. Your doctor will develop a personalized treatment plan to meet your specific needs.
Insurance Coverage:
DVT treatment costs can vary, but most health insurance plans cover these treatments. Verify with your insurance provider for specific coverage details.
Success of Minimally Invasive Treatments:
Minimally invasive treatments, such as catheter-directed thrombolysis, show high success rates with minimal complications. Consult your doctor to determine if these options are suitable for your case.
Conclusion:
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious condition that demands prompt treatment to prevent severe health issues. Seek immediate medical care if you experience symptoms. Treatment options include anticoagulants, compression stockings, and interventional procedures. Personalized treatment plans will be developed with your doctor to address your specific needs and goals.